Knee pain affects millions of people worldwide and can slowly take away the joy of everyday movement. Simple actions like walking, standing, or climbing stairs may become painful, especially for older adults or those with arthritis or past injuries. When medications, injections, or physiotherapy stop working, knee replacement surgery can help restore comfort and mobility—allowing patients to return to an active, independent life.
Understanding Knee Replacement Surgery
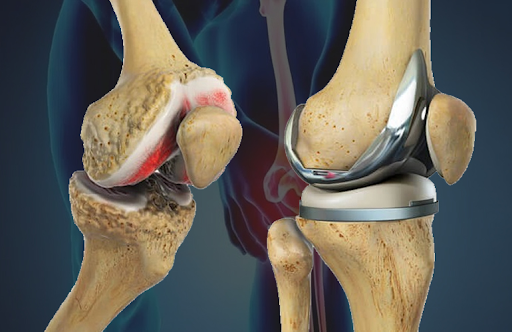
Knee replacement surgery, medically called knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee joint and replacing them with specially designed artificial components. These implants are usually made from high-quality metal alloys, durable plastic, or ceramic materials and are built to mimic the movement of a natural knee.
Over the years, improvements in surgical techniques and implant design have made this procedure safer, more reliable, and longer-lasting.
Who May Need Knee Replacement?
Doctors may recommend knee replacement surgery if a patient:
- Has advanced osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or joint damage from injury
- Experiences ongoing knee pain, even while resting
- Struggles with daily activities like walking or standing
- Notices knee deformities such as inward or outward bending
- Finds no relief from non-surgical treatments like medication or physiotherapy
Different Types of Knee Replacement Procedures
The type of surgery depends on the severity and location of joint damage:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): The entire knee joint surface is replaced. This is the most commonly performed option.
- Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): Only the affected portion of the knee is replaced, preserving healthy bone and tissue.
- Revision Knee Replacement: Required when an existing implant wears out, loosens, or develops complications.
- Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement: Uses smaller incisions, resulting in reduced tissue damage and faster recovery for suitable patients.
How the Surgery Is Performed
Knee replacement surgery usually takes one to two hours and follows these general steps:
- The patient receives spinal or general anesthesia
- A surgical incision is made to access the knee joint
- Damaged bone and cartilage are removed
- Artificial implants are carefully positioned
- The incision is closed, and post-operative care begins
After surgery, patients are monitored in the hospital before starting rehabilitation.
Also know: Knee Pain in Young Adults: Hidden Causes & Modern Treatments
Recovery and Rehabilitation Timeline
Healing after knee replacement is gradual and depends on individual health and commitment to physiotherapy.
- First 1–2 weeks: Walking with assistance and gentle exercises
- Up to 6 weeks: Improved flexibility, reduced pain, and better joint movement
- 3–6 months: Return to most daily activities with minimal discomfort
- 1 year and beyond: Continued strengthening and stability, with implants often lasting 15–20 years or more
Consistent rehabilitation, weight management, and following medical advice play a key role in long-term success.
Benefits of Knee Replacement Surgery
Patients often experience:
- Significant and lasting pain relief
- Better joint movement and flexibility
- Correction of knee deformities
- Improved independence and mobility
- A noticeable improvement in overall quality of life
Why Many Patients Choose India
India has emerged as a preferred destination for orthopedic procedures due to skilled surgeons, advanced hospitals, and modern technology. One major advantage is the knee replacement surgery cost in India, which is considerably lower than in many Western countries—while maintaining high standards of safety and care.
Possible Risks and Precautions
Although knee replacement is generally safe, potential risks include infection, blood clots, stiffness, or implant wear over time. These complications are uncommon and can be minimized through experienced surgical care, regular follow-ups, and proper rehabilitation.
Final Words
Knee replacement surgery is not just about relieving pain—it’s about reclaiming freedom of movement and confidence in daily life. With the right medical team, advanced techniques, and a structured recovery plan, patients can enjoy long-term relief and a more active, comfortable future.